Isosurfaces can be made in two types of displays, regular isosurfaces, and isosurfaces colored by another parameter. An isosurface is a 3D surface mapping the location of a single parameter value through a 3D field. Isosurfaces are a 3D analog of a single contour line in a 2D plot; the intersection of an isosurface and any plane is a contour line of the same value in that plane.
Coloring an isosurface by another parameter can serve many purposes. One example use of this is creating a display for possible icing conditions in the atmosphere that could be useful for pilots. To do this, you would select Temperature as your field, the "Isosurface colored by another parameter" display type, and Relative Humidity in the Field Selector window that appears when you click Create Display. After the display is created, you can set the isosurface value for Temperature to be 0 degrees Celsius in the Layer Controls tab of the Data Explorer. Now, in the Main Display window, you have a surface of 0 degrees Celsius colored by Relative Humidity. Wherever you see high RH values means that there is a lot of moisture in the atmosphere, and at the freezing temperatures, there could be icing conditions.
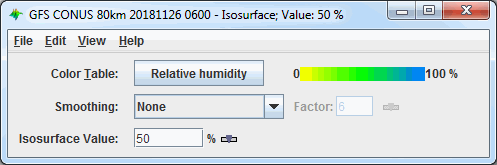
Image 1: Isosurface Controls Properties Dialog
- Color Table - Shows the active color table and the associated high and low data values in the units of the display. As the mouse pointer is moved over the color bar, the value at a particular color is shown. Right click on the color bar or click on the button that displays the name of the Color Table to make modifications to the color bar. This allows you to open the Color Table Editor, change the range, select other color tables, etc.
- Smoothing - Smooths the grid that can be used to smooth contour lines or flow fields in the display. There are seven types of smoothing: None, 5-point, 9-point, Gaussian, Cressman, Circular, and Rectangular weighted smoothers. The smoothing factor can be adjusted for all except the 5-point and 9-point smoothers. The higher the value, the smoother the grid. For the Cressman, Circular and Rectangular aperture smoothing types, the smoothing factor is the radius in grid spacing units.
- Isosurface Value - Sets the numerical value of your field that the display will draw the isosurface at. You can do this by clicking the
 button or entering a
value in the field and hitting Enter.
button or entering a
value in the field and hitting Enter.
- Contour - Opens the Contour Properties Editor to change how the contours appear in the Main Display window. This is an option for the Color-Filled Contour Plan View display type.
- Visible Range - Sets the range of the data displayed. These numbers represent the range of reflectivity values that can be viewed in the Main Display window. This tool is active when the Visible Range checkbox is checked, if not checked, the default range will be used. To change these values, check the checkbox, and click
 to bring up a Change Visible Range window, where you can enter your upper and lower bound values.
to bring up a Change Visible Range window, where you can enter your upper and lower bound values. - Texture Quality - Sets the quality of the displayed texture of Image Control. A higher quality will take longer to render and more memory.
- Smoothing - Smooths the grid that can be used to smooth contour lines or flow fields in the display. There are seven types of smoothing: None, 5-point, 9-point, Gaussian, Cressman, Circular, and Rectangular weighted smoothers. The smoothing factor can be adjusted for all except the 5-point and 9-point smoothers. The higher the value, the smoother the grid. For the Cressman, Circular and Rectangular aperture smoothing types, the smoothing factor is the radius in grid spacing units.
- Levels - Lists the native grid levels. Click on one level value to reset the plan to that level. The plan level in use is shown in the data's native altitude units. The Levels box is editable. Click in the box, enter a value and hit Enter to set your own value. Additionally, you can click on the arrows to the right of the Levels box to switch levels, or click on the Cycle checkbox to animate vertically through all available levels. This is an option for the Contour Plan View, the Color-Filled Contour Plan View, and the Color-Shaded Plan View display types.
- Vertical Range - Sets the vertical extent of the data with respect to the wireframe box of the Main Display window. Click the
 button to set the vertical range of the data. This works similarly to the Vertical Range in the Main Display window, which sets the height of the wireframe box for other types of data. Changing these values can allow certain features to stand out more by showing higher peaks and valleys based off of their data values.
button to set the vertical range of the data. This works similarly to the Vertical Range in the Main Display window, which sets the height of the wireframe box for other types of data. Changing these values can allow certain features to stand out more by showing higher peaks and valleys based off of their data values. - Display -
- Shade Colors - Colors every pixel to give a smooth gradation of color. The alternative is coloring an area of pixels corresponding to a single data grid cell with one color.
- Mode - Sets the way the texture of the data is displayed. You can select Solid, Mesh, or Points. This is useful for looking at the structure of the underlying data.
- Point Size - Sets the size of the points when the Mode Points is chosen.
Many of the menu items seen utilizing this display are standard options that can be found in the Menus section of the Layer Controls page. However, there is one option that is unique to this display.
The Edit menu has this unique option:
- Levels - Represents the level where the data is displayed. This is an option for the *As Topography display types.
The View menu has these unique options:
- Use Data Projection - Re-centers the display and resets the zoom level back to the display's initial settings without changing any other preferences you have modified.
- Use Grid Projection - Re-centers the display and resets the zoom level back to the display's initial settings without changing any other preferences you have modified. This is an option for the *As Topography display types.