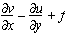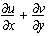McIDAS-X User's Guide
Version 2020.1
[Search Manual]
[Table of Contents]
[Go
to Previous]
[Go
to Next]
GRDCOPY
Copies
grids from one dataset to another.
Format
GRDCOPY sdataset ddataset [keywords]
Parameters
sdataset |
source
ADDE dataset name and absolute position; specify one of the following
formats: |
|
|
group/descriptor.position
alias.position |
|
only
positive integers or ALL (all positions) are valid for position (no
default for group/descriptor or alias; default=ALL for position) |
ddataset |
destination
ADDE dataset name and absolute position; specify one of the following
formats: |
|
|
group/descriptor.position
alias.position |
|
use
only positive integers for position |
Search Keywords
DAY= |
d1
. . dn |
copies
grids with the specified days |
DRAnge= |
bday eday inc |
copies
grids in the range of days bday through eday, incremented
by inc days (no default for bday; eday default=bday; inc default=1) |
ENSemble= |
e1 . . en |
copies grids with the specified ensemble numbers; each ensemble number must include a + or - sign,
e.g., -1 -0 +0 +1 |
FDAy= |
copies
grids with the specified forecast day; a grid's forecast day is determined
by adding the forecast hour to the day and time; for example, a 12 UTC
grid from day 95300 with a forecast hour of 72 has a forecast day of
95303; you cannot use FDAY with the FHOUR, FRANGE or MATH keyword |
FHOur= |
h1
. . hn |
copies
grids with the specified forecast hours; you cannot use FHOUR with the
FRANGE, FDAY or FTIME keyword |
FRANGe= |
bhr ehr inc |
copies
grids in the range of forecast hours bhr through ehr, incremented
by inc hours; you cannot use FRANGE with the FHOUR, FDAY or
FTIME keyword (no default for bhr; ehr default=bhr; inc default=1) |
FTIme= |
copies
grids with this forecast time; a grid's forecast time is determined by
adding the forecast hour to the time; for example, a 12 UTC grid with
a forecast hour of 18 has a forecast time of 6 on the following day;
you cannot use FTIME with the FHOUR, FRANGE or MATH keyword |
GPRo= |
g1
. . gn |
copies
grids with the specified projection, for example, MERC, PS, LAMB, EQUI |
GRIB= |
geo par model level
copies
grids with the specified GRIB codes; the four values are the geographic,
parameter, model and level codes that can be listed with GRDLIST
FORM=ALL;
values specified as an X (a placeholder) or not specified at all will
match any GRIB code |
GRId= |
bgrid egrid |
copies
grids bgrid through egrid; enter a grid number or
LAST (last grid) for bgrid and egrid; see the Remarks
(no default for bgrid; egrid default=bgrid) |
LEV= |
l1[u1]
. . ln[un] |
copies
grids with the specified levels and units, e.g., SFC, 850[MB], 5000[M];
units are optional but must be in square brackets if specified; if [MB] or [HPA] is specified for units then grids
with either of those units are copied; if [NONE] is specified for units then grids with no assigned units are copied |
PARam= |
p1
. . pn |
copies
grids with the specified parameters, for example, T, Z, RH; see the Remarks |
SRC= |
s1
. . sn |
copies
grids with the specified sources, for example, MDX, GFS, ETA |
TIMe= |
t1
. . tn |
copies
grids with the specified times |
TRAnge= |
btim etim inc |
copies
grids in the time range of btim through etim, incremented
by inc (no default for btim; etim default=btim; inc default=1,
meaning one hour) |
Derived Grid Keywords
DERive= |
derives
a grid of the specified parameter, for example, DST or VOR; searches
for the component grids using the search keywords, derives the grid,
and copies it to the ddataset; do not use with the PARAM keyword; see
the Remarks |
MERidional= |
YES |
adds
a correction term to account for the convergence of longitude lines at
the poles |
|
NO |
does
not add a correction term; only valid with DERIVE=ABV, DSH, DST, DVG,
or VOR; see the Remarks (default) |
PLAnet= |
planet
for which derive calculations are done; valid options are MERCURY, VENUS,
EARTH, MARS, JUPITER, SATURN, NEPTUNE, URANUS (default=EARTH) |
Mathematical Operations Keywords
Gn= |
'clause1; clause2; .
.; clausen'
grids to be used with the MATH keyword; separate select clauses with
semicolons; single quotes are mandatory; specify clause using
the following format:
valid
options for searchkeyword are DAY, FHOUR, GPRO, GRID, LEV, PARAM,
SRC, TIME; you can specify numbers between 1 and 99 in the keyword name
(G1, G2, . . , G99); see the Remarks |
INFo= |
'text' |
string
placed in the header of the copied grid when the MATH keyword is used;
maximum of 48 characters |
MATh= |
'expression' |
mathematical
operation to perform on the grids specified with the Gn keywords;
single quotes are mandatory; see the Remarks |
NEWpar= |
param punit level lunit src
header information for the grid copied with the MATH keyword; parameter
and level values, and associated units |
|
|
param |
grid
parameter; four characters maximum (default=MATH) |
|
|
punit |
units
of grid parameter; four characters maximum (default=NONE) |
|
|
level |
grid
level (default=from grid) |
|
|
lunit |
units
of grid level; two characters maximum (default=from grid) |
|
|
src |
grid
source; four characters maximum (default=from grid) |
Output Keywords
BYTecount= |
YES |
lists
the number of bytes received from the server |
|
NO |
does
not list the number of bytes (default) |
DEL= |
YES |
delete
the destination grid file before copying; see the Remarks |
|
NO |
do
not delete the destination grid file (default) |
DGRid= |
beginning
grid number in the destination grid file to place the copied grids; this
keyword may overwrite existing grids; see the Remarks (default=append
after the last grid in the grid file) |
MAXgrd= |
maximum
number of grids the newly created destination grid file can store; see
the Remarks (default=1000) |
NUM= |
number
of grids matching the criteria defined with the search keywords to copy;
for example, if you specify NUM=50, the first 50 grids matching the search
keywords are copied (default=1) |
|
ALL |
copies
all grids matching the search keywords |
PUNit= |
units to assign to the pressure grids that are output;
the valid options are MB or HPA and will be used regardless of which of the two units appear in the source
grids (default=units in source grids) |
SUBsect= |
slat nlat elon wlon incrow inccol
geographic
region to subsect from the source grid, and row and column reduction
intervals to use within the subsect region; see the Remarks |
|
slat,
nlat |
southern
and northern latitudes of the subsect region |
|
elon,
wlon |
eastern
and western longitudes of the subsect region (slat, nlat, elon, wlon defaults=source
grid bounds) |
|
incrow, inccol |
row
and column reduction intervals; 1 means copy every row/column of grid
points in the subsect region, 2 means copy every other row/column, etc.;
when subsecting a conformal projection grid, the incrow and inccol values
must be the same (default=1 for both) |
|
Note:
If the source grid is a McIDAS grid, you can subsect it by row and column
instead of latitude and longitude. To do so, specify row and column numbers
instead of latitudes and longitudes in the first four parameters, and
specify ROWCOL as the seventh parameter. For example, SUBSECT=10 40 80
160 1 2 ROWCOL uses rows 10, 11, 12, ..., 40 and columns 80, 82, 84,
..., 160 for the subsect region. (If you don't include the ROWCOL at
the end, it will treat 10 and 40 as latitudes, and 80 and 160 as longitudes.) |
TITLE= |
'text'
|
title
of the newly created destination grid file; 32 characters maximum; see
the Remarks |
Remarks
Individual
grids are stored in grid files. Each dataset position points to a single grid
file. GRDCOPY copies grids from one or more grid files in the source dataset
to a single grid file in the destination dataset.
If you specify
DEL=YES or a position number of a nonexistent grid file in the ddataset parameter,
the grids are copied into a newly created grid file with the attributes specified
in keywords MAXGRD and TITLE.
Using the DGRID
keyword may result in grids being overwritten in the destination grid file.
For example, if the destination grid file has 50 grids (in grids 1 to 50) and
you specify NUM=10 DGRID=25, the new grids will overwrite grids 25 to 34 in
the destination grid file.
The GRID keyword
copies grids from the grid file specified with the sdataset position number;
the default position value, ALL, is not valid. When using the GRID
keyword, do not specify additional search keywords, PARAM, LEV, DAY, etc.,
or NUM.
If you specify
PARAM=STREAML, WINDB or WINDV, GRDCOPY does not search for grids with that
parameter. Instead, it locates the u-component grids that match the other search
keywords, then locates the matching v-component grids, and copies both sets
of grids to the destination dataset. These grids may be used to draw streamlines,
plot wind barbs or plot wind vectors with the GRDDISP command. If you specify
any other parameter with the PARAM keyword, the value entered is the value
searched for in the grid's parameter field.
Use command
GRDLIST to preview the grids to be copied with GRDCOPY.
Use the SUBSECT
keyword to copy a portion of the source grid. This keyword is useful because
the subsected grid is smaller and can be copied more quickly than the source
grid.
Use the DERIVE
keyword to create grids of a variety of common meteorological parameters. The
valid options are defined in the table below. In these equations, the following
variables appear often:
u =
u-component of the wind
v =
v-component of the wind
x =
grid point distance in the east-west direction
y =
grid point distance in the north-south direction
| DERIVE= |
Description |
Equation |
| ABV |
absolute
vorticity |
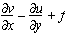
f =coriolis
parameter: 2ΩsinΦ (see
COR) |
| BETA |
beta
parameter |

f =coriolis
parameter: 2ΩsinΦ (see
COR)
Ω=angular
speed of the rotation of the planet (7.292 × 10-5 radians/second for Earth)
Φ=latitude
in degrees
a=radius
of the planet |
| COR |
coriolis
parameter |
2ΩsinΦ
Ω=angular
speed of the rotation of the planet (7.292 × 10-5 radians/second for Earth)
Φ=latitude
in degrees |
| DIR |
wind
direction |
atan2(-u,-v) |
| DSH |
shearing
deformation |
 |
| DST |
stretching
deformation |
 |
| DVG |
divergence |
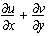 |
| SPD |
wind
speed |
 |
| TD |
dew
point temperature |

T =temperature
in Kelvin
RH =relative
humidity
Rv=moist
gas constant: 461.5 Joules per kilogram per degree Kelvin |
| VOR |
relative
vorticity |
 |
Use the MERIDIONAL
keyword to correct for the convergence of longitude lines at the poles. When
deriving divergence and stretching deformation grids (DVG and DST), specify
MERIDIONAL=YES to subtract the following correction term from the calculation.

When deriving
vorticity, absolute vorticity, or shear deformation grids (VOR, ABV, or DSH),
specify MERIDIONAL=YES to add the following correction term to the calculation.

For both the
correction terms above:
u =
u-component of the wind
v =
v-component of the wind
Φ =
latitude in degrees
r =
radius, in kilometers, of the planet at Φ latitude
The MERIDIONAL
keyword has no effect with other DERIVE keyword options.
Use the Gn keywords
to specify the grids to be used with the MATH keyword. Each Gn keyword
specifies a single grid. Gn is followed by a list of select clauses
in single quotes. By default, subsequent Gn keywords have the same
select clauses, unless specified differently. For example, to request 850 and
1000 mb height grids from the 0:00 UTC GFS run, specify
G1='LEV 850;PARAM Z;TIME 0;SRC GFS' G2='LEV 1000'
The MATH keyword
defines the operation to perform on the specified grids, for example, MATH='G1**(SQRT(G2))'.
The table below shows the operations available with the MATH keyword.
| MATH= option |
Function |
| + |
addition |
| – |
subtraction |
| * |
multiplication |
| / |
division |
| ** |
power |
| SQRT |
square
root |
| EXP |
exponential
(the number e raised to a power) |
| LOG |
natural
logarithm |
| LOG10 |
base
10 logarithm |
| SIN |
sine |
| COS |
cosine |
| TAN |
tangent |
| ASIN |
arcsine |
| ACOS |
arccosine |
| ATAN |
arctangent |
| ABS |
absolute
value |
| MIN |
minimum
of two grids |
| MAX |
maximum
of two grids |
| DDX |
derivative
with respect to x |
| DDY |
derivative
with respect to y |
| DELSQ |
laplacian |
| COR |
coriolis
parameter (2ΩsinΦ) |
| BETA |
beta parameter  |
| LAT |
creates
a grid of latitude |
| LON |
creates
a grid of longitude |
When specifying
powers of ten, such as 102 or 10-3 in the MATH keyword,
use one of the two methods shown in the examples below.
MATH='2*7.292*(1e-5)*(SIN(G1))'
MATH='2*7.292*(10**(-5))*(SIN(G1))'
In these entries
both 1e-5 and 10**(-5) represent 10-5. You must include the parentheses
with 10**(-5); 10**-5 will not be interpreted correctly.
When using
the MATH keyword and the range of output data values is larger than five orders
of magnitude, the output grid is scaled based on the maximum end of the range.
This means that small data values may be replaced by zeros in the output grid.
Grids created
using GRDCOPY and those created using IGG MAKE with the DERIVE or MATH keyword
may not yield numerically identical results. However, the values for both are
correct. The differences are the result of one of the following:
- Grids created
using GRDCOPY will be in Standard International units, whereas grids created
using IGG MAKE may not be. For example, a grid created using the TADV (temperature
advection) function in IGG MAKE will be in degrees per day, while a similar
grid created using GRDCOPY with the MATH keyword will be in degrees per second
unless a factor is added to the equation to compute it in degrees per day.
- By default,
IGG MAKE applies a smoothing function and, if applicable, a meridional correction
term to the data. GRDCOPY does not do this by default. You can override the
IGG MAKE defaults by specifying SMO=NO and ADD=NO.
Examples
GRDCOPY NCEP/GFS MYDATA/GRIDS.1
This entry
copies the first grid in the first grid file in dataset NCEP/GFS to the grid
after the last grid in position 1 of dataset MYDATA/GRIDS.
GRDCOPY NCEP/GFS.5 MYDATA/GRIDS.2 LEV=850 NUM=10 DGRID=5
This entry
copies the first 10 grids with a level of 850 mb in position 5 of dataset NCEP/GFS
to grids 5 through 14 in position 2 of dataset MYDATA/GRIDS.
GRDCOPY NCEP/GFS.5 MYDATA/GRIDS.1 NUM=ALL DEL=YES TITLE='All grids
in NCEP/GFS position 5'
This entry
copies all grids in position 5 of dataset NCEP/GFS to position 1 of dataset
MYDATA/GRIDS. The keyword DEL=YES deletes the existing destination grid file
and creates a new file with the title All grids in NCEP/GFS position 5 for
the copied grids. Since the destination grid file is new, the copied grids
begin in grid 1. Be careful when using NUM=ALL; grid files can contain thousands
of grids. Use the search keywords to copy only the desired grids, as shown
in the following examples.
GRDCOPY NMC/ETA.ALL G/SCRATCH.10 LEV=500 PARAM=Z T TD RH ABV DAY=#Y
TIME=0 NUM=ALL
This entry
copies all 500 mb height, temperature, dew point temperature, relative humidity
and absolute vorticity grids from today's 00 UTC run in all grid files in dataset
NMC/ETA to position 10 of dataset G/SCRATCH. The grids are appended after the
last grid in the destination grid file.
GRDCOPY NMC/ETA.1 G/MODEL.2 LEV=TRO PARAM=Z T FHOUR=12 36 NUM=ALL
DGRID=1
This entry
copies all 12- and 36-hour forecast tropopause height and temperature grids
in position 1 of dataset NMC/ETA to position 2 of dataset G/MODEL. The copied
grids begin in grid 1 of the destination grid file.
GRDCOPY NMC/ETA.1 G/MODEL.2 LEV=TRO PARAM=Z T FRANGE=12 36 6 NUM=ALL
DGRID=100
This entry
copies all 12-, 18-, 24-, 30-, and 36-hour forecast tropopause height and temperature
grids in position 1 of dataset NMC/ETA to position 2 of dataset G/MODEL. The
copied grids begin in grid 100 of the destination grid file.
GRDCOPY NMC/ETA.1 G/MODEL.2 LEV=TRO PARAM=Z T FDAY=#Y FTIME=18 NUM=ALL
This entry
copies all forecast tropopause height and temperature grids valid at 18 UTC
today in position 1 of dataset NMC/ETA to position 2 of dataset G/MODEL. The
grids are appended after the last grid in the destination grid file.
GRDCOPY MODEL.5 GRD.1 GRID=1 20 DGRID=1
This entry
copies grids 1 through 20 in position 5 of the dataset with the alias name
MODEL to grids 1 through 20 in position 1 of the dataset with the alias name
GRD.
GRDCOPY GRIDS/GFS CASE/STUDY.1 DAY=#Y TIME=12 PARAM=U V LEV=200 SUBSECT=-20
20 -180 -120 1 2 NUM=ALL
This entry
copies all 200 mb height u- and v-component grids from today's 12 UTC run in
dataset GRIDS/GFS to position 1 of dataset CASE/STUDY. The copied grids contain
every source grid point in the row direction and every other source grid point
in the column direction in the region 20°S to 20°N and 180°E to
120°E.
GRDCOPY GG.1 GRD.4000 DERIVE=SPD LEV=500 FHOUR=48
The entry creates
a 500 mb wind speed grid using component grids in position 1 of the dataset
with the alias GG. The grids used to derive wind speed are the u- and v-components
of the wind with 48-hour forecast times. The derived grid is copied to position
4000 of the dataset with the alias GRD.
GRDCOPY RTGRIDS/GFS LOCAL/MYGRIDS.10 DERIVE=VOR LEV=500 DAY=96284
TIME=12 FHOUR=12 24 36 48 NUM=ALL
This entry
creates 500 mb relative vorticity grids using component grids from dataset
RTGRIDS/GFS. The grids used to derive relative vorticity are the u- and v-components
of the wind from day 96284 at 12:00 UTC with 12-, 24-, 36-, and 48-hour forecast
times. The derived grids are copied to position 10 of the dataset LOCAL/MYGRIDS.
GRDCOPY GRD.8000 GRD.4000 G1='PARAM Z;LEV 850;FHOUR 48' G2='LEV 1000'
MATH='G1-G2' NEWPAR=THCK
This entry
finds two 48-hour forecast geopotential height grids in position 8000 of the
dataset with the alias GRD. The 1000 mb grid is subtracted from the 850 mb
grid and the result is copied to position 4000 of the dataset with the alias
GRD. The copied grid is labeled with the new parameter name THCK and units
NONE.
GRDCOPY GRD.4004 GRD.4004 G1='PARAM T;LEV 1000' G2='LEV 850' G3='PARAM
U;LEV 1000' G4='LEV 850' NEWPAR=M DEG MATH='(COR(G1))/9.8*((G1+G2)/2)*((G3-G4)/(G1-G2))'
This entry
creates a grid of frontal slope (Margules equation) from the 1000 and 850 mb
temperature grids, and the 1000 and 850 mb u-component grids in position 4004
of the dataset with the alias GRD. The grid is copied into the same dataset,
and labeled M with units DEG.
GRDCOPY G/G.4000 G/G.4000 G1='PAR T;LEV 1000;TIME 12; DAY 93070;SRC
GFS' G2='PAR U;SRC ROI' G3='PAR V; SRC ROI' MATH='-(G2*(DDX(G1))+G3*(DDY(G1)))'
INFO='Temperature Advection at 1000 MB' NEWPAR=TADV K/S
This entry
creates a grid of 1000 mb temperature advection using the 1000 millibar GFS
model temperature grid, and the 1000 mb ROI model u- and v-component grids
in position 4000 of the dataset G/G. The grid is copied into the same dataset,
and labeled TADV with units of degrees Kelvin per second. The string Temperature
Advection at 1000 MB is placed in the header of the new grid.
[Search Manual]
[Table of Contents]
[Go
to Previous]
[Go
to Next]