Image 1: Data Sources Tab of the Data Explorer
This section describes how to make displays using NWS WSR-88D Level II data. The steps include:
The Level II data is supplied as volume-scan files, each file having all data from WSR-88D radar for all sweeps for one "time". Archived Level II data is available from the National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) (data from NCDC must be un-tarred).
The files should be stored on your local file system with each station's files in a directory whose name is the 4-character ID (e.g., KTLX for Oklahoma City). In many cases, the data files do not have any location information in them and McIDAS-V uses the directory name as a first guess at the station location.
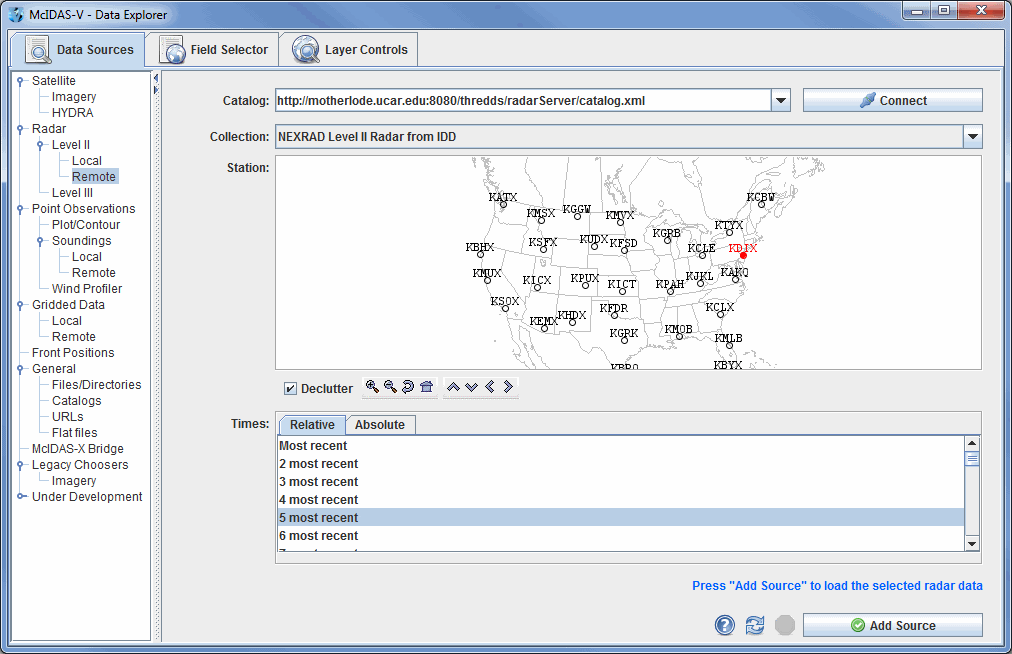
In the Data Sources tab of the Data Explorer, select Radar->Level II->Remote to view the Level II radar chooser. The Radar->Level II->Local chooser allows you to choose Level II data from your file system. For more information about the Level II radar chooser, see Choosing NEXRAD Level II Radar Data.

Select a station and a relative or absolute set of times. When done, click the ![]() button.
button.
The data source is shown in the Field Selector tab of the Data Explorer. Level II data has three moments or data types: Reflectivity, RadialVelocity, and SpectrumWidth. McIDAS-V has several display types for Level II data, and any of the moments can be shown with any of the displays. Selecting "Reflectivity" in the Fields panel will show the list of available displays in the Displays panel.
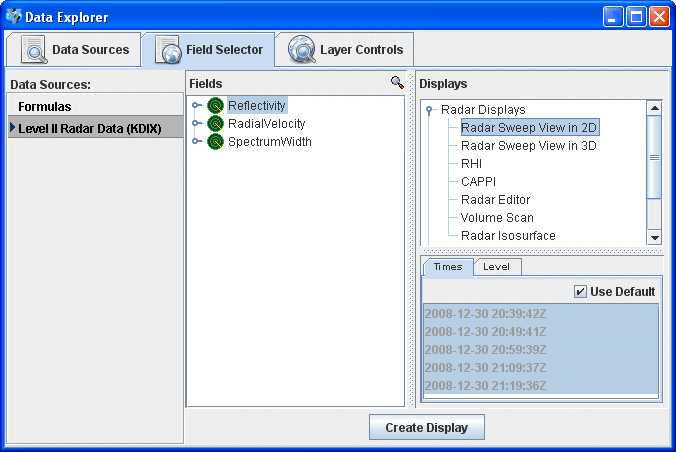
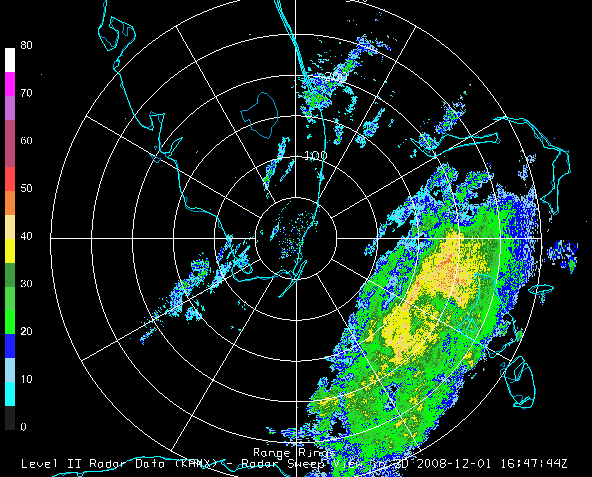
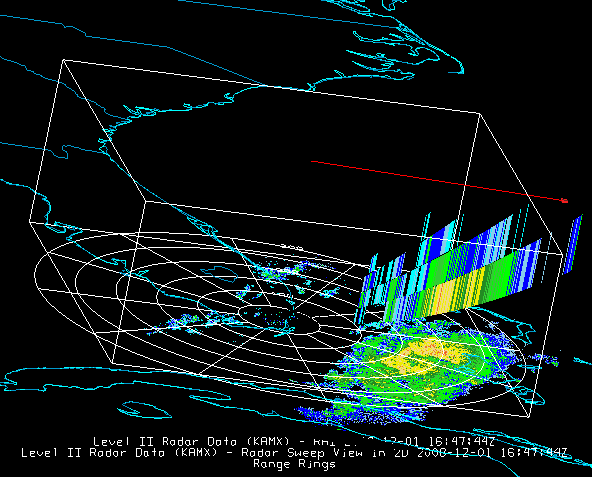
Select the Radar Sweep View in 2D under Radar Displays in
the Displays panel and click ![]() . Radar
Sweep View in 2D plots the data as a colored image on the base of
the 3D display area.
. Radar
Sweep View in 2D plots the data as a colored image on the base of
the 3D display area.
The Radar Sweep Controls allow you to change which sweep elevation you want to use. You can add range rings with the Displays->Add Range Rings menu item.
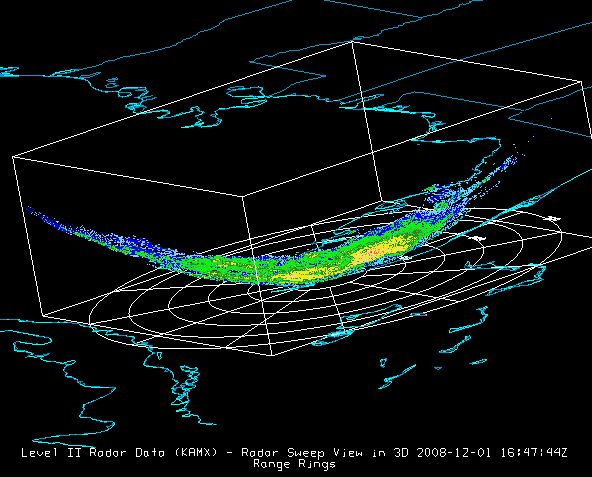
Select the Radar Sweep View in 3D entry under Radar Displays in the Displays panel. The Radar Sweep View in 3D display plots the data as a colored image, with the data plotted in 3D space at the elevation where the sweep occurred. You can rotate the display to see its 3D nature.
You can use this display to merge radar data displays with upper air data, such as McIDAS-V plots of NOAA Profiler data. Since the Earth is projected onto a flat surface in this display, the sweep has a shape very close to a rotated parabola. The Elevation Angles menu in the Layer Controls tab allows you to change which sweep elevation to display.
Select RHI (Range-Height Indicator) under Radar Displays in the Displays panel and press Create Display. The RHI display plots the data as a colored vertical cross section at the true elevations of the beams in 3D space (Image 5). This pseudo-RHI is constructed from several horizontal sweeps of the radar. It may be necessary to rotate the display to see the RHI in 3D.
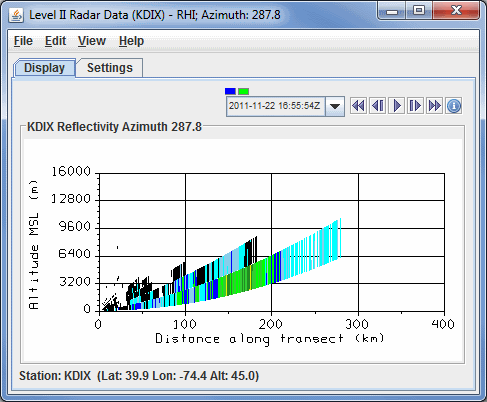
The beam width is indicated by the vertical extent of each colored vertical stripe, corresponding to a bin beam bin sample. The position of the RHI in azimuth can be adjusted by dragging the little box on the end of the selector line above the RHI.
A 2D plot of pseudo-RHI (Image 6), is shown in the Display tab of the Layer Controls tab. The RHI displays have an auto-rotate feature and a Time Animation Widget.
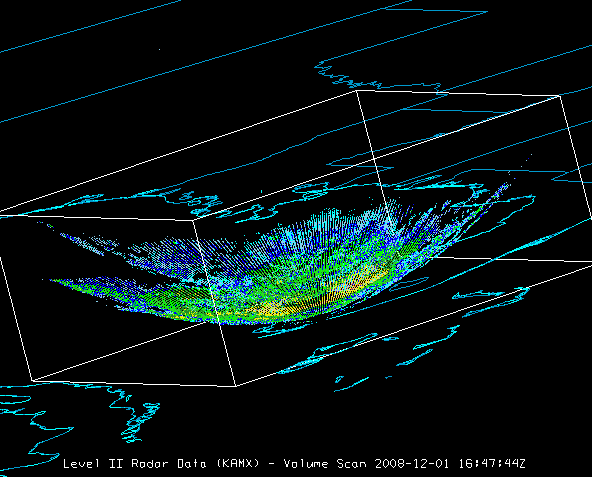
Select Volume Scan (all sweeps) in the Displays panel in the Field Selector. Volume Scan (all sweeps) plots the data as 3D field of points colored by value. Each point is a bin value; all sweeps and bins are shown.
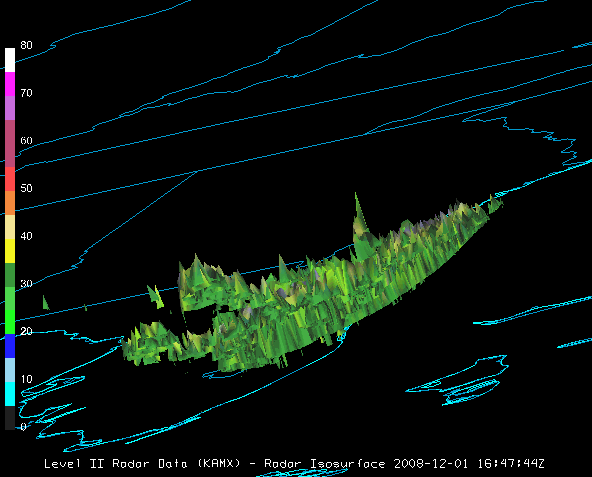
Select Radar Isosurface under Radar Displays in the Displays panel in the Field Selector tab. An isosurface is a 3D analog of a contour line which shows the location of all data with a single data value. Interpolation is used between sweep altitudes in the isosurface plot of Level II data, and all data in a volume scan is used.
To select Level II data from the Radar Imagery->Level II->Local file chooser:
For more help with displaying Level II radar imagery, please see the Level II Radar Imagery tutorial on the McIDAS-V Documentation webpage.